Due diligence: importance, process, types and costs [incl. checklist].
Due diligence occupies a special position in the entire M&A process. It represents a comprehensive company audit the outcome of which will have a decisive influence on the further course of the negotiations. Although they alone do not guarantee the success of a Company sale can guarantee, it is nevertheless an important basis. So it is not surprising that it is usually given a lot of attention.
This article explains both the formal meaning and Objective of the due diligence as well as the Procedure in practice. Last but not least, we provide an overview of the various Types of due diligence, including vendor due diligence ? more on this below.
A Vendor Due Diligence (VDD) is the inspection of a sales object on behalf of the seller.
We also provide guidance for Time and Costs and the Scope in the form of a due diligence checklist.
Due Diligence Definition: What is Due Diligence?
Due diligence is a fundamental term in the M&A sector and refers to a comprehensive review process that examines all relevant aspects of a company. This process is an essential part of transaction preparation and helps to identify the risks and opportunities of a potential takeover.
What does due diligence mean in German?
The English term “due diligence” is also used in this form in German-speaking countries, but can also be translated as “due diligence”. Due care in traffic’ or ‘Duty of care’. translate. It is also easier to use the following formulation in conversation ?careful examination? use. The buyer thus checks all details about the company offered by the seller.What is the aim of a due diligence audit?
In principle, each due diligence can have an individual focus. The idea of due diligence is not limited to specific areas. The overriding However, the aim is always to determine the opportunities and risks of an M&A transaction and ideally to limit them.
The information of a DD is important to decide whether a purchase or sale can take place at all and on what terms the Company purchase agreement is possible.Due diligence audits: Advantages and disadvantages
In principle, each due diligence can have an individual focus. The idea of due diligence is not limited to specific areas. The overriding However, the aim is always to determine the opportunities and risks of an M&A transaction and ideally to limit them.
The information of a DD is important to decide whether a purchase or sale can take place at all and on what terms the Company purchase agreement is possible.Advantages of due diligence:
Disadvantages of due diligence:
What is being tested?
There are no fundamental restrictions as to which documents can be inspected in the course of a due diligence review. In the usual case, the buyer and his M&A consulting Documents provided to them by the seller either in file folders or in a safe, secure and internet-based platform also called a data room.
In most cases, these are tax-related, Legal and financial (as well as other, if applicable) documents, records and contractswhich are checked in detail. This results in further questions that the seller should answer truthfully. Particularly sensitive persons, customers or company data may also be neutralised and are then revealed via a ‘key’ in the final purchase contract.
What is the Due Diligence Report?
The due diligence report usually consists of three main parts: a Summary, a financial analysis and an assessment of the potential risks and opportunitiesassociated with the transaction. The report often also includes an analysis of the company’s competitive position, a review of legal obligations and risks, and a review of management and, if available, corporate governance.
The executive summary provides an overview of the due diligence process and summarises the conclusions of the investigation. It is important to note that the Summary not a substitute for the full report should be considered.
The summary should be sufficiently detailed to enable readers of the report to understand the basic findings of the study.
In detail: What is Enhanced Due Diligence?
Enhanced due diligence (EDD) is a Important aspect of the Know Your Customer (KYC) process. It is a process designed to help financial institutions and other organisations identify and understand their customers and the risks they pose. It is applied to transactions that are particularly large and relevant to an industry. The vast majority of transactions do not have this scale.
It is used to assess the potential to be used in Money laundering, terrorist financing and other illegal activities to be involved. Enhanced Due Diligence is a comprehensive process that includes seven important steps. These steps are:
- Identification and verification of the client
- Assessing the source of the client’s assets and funds
- Assessment of the client’s business activities
- Determine the risk profile of the client
- Investigation of the identity of the customer
- Review of the client’s financial information
- Performing a background check
Each of these steps must be taken to fully complete the EDD process. All due diligence steps must be completed in order to properly assess the client’s risk.
Due Diligence Checklist
If you would like to know which points are checked in detail, we recommend that you take a look at our Due Diligence Checklist to throw.
Where in the sales process does due diligence take place?
Typically, due diligence is carried out following the signing of the ‘Letter of Intent’. initiated. The LoI represents a milestone in the M&A process which expresses a clear interest of both parties and contains important elements for the subsequent purchase contract.
On this basis of trust, the sensitive documents can be released for review. Thus the Due diligence audit a crucial audit componentin order to be able to present a basis for the subsequent negotiations.Who carries out due diligence?
Although both the buyer and the seller can initiate a due diligence process, it is usually the potential buyerswho carries it out. The exception is a so-called vendor due diligence (VDD) by the seller.
Do the documents provided by the seller also disclose all risks? In many cases, the prospective buyer hands over an extensive catalogue of questions to the seller in advance. The seller then prepares the inspection of the documents.
What is not asked and has no significant relevance does not have to be presented.
While the buyer initiates the due diligence, he hardly carries it out independently from an operational point of view. Depending on the individual M&A use case, the a team of specialists is required to be able to check all the documents competently. It so happens that Lawyers, tax advisors and also M&A advisors are used by the buyer.
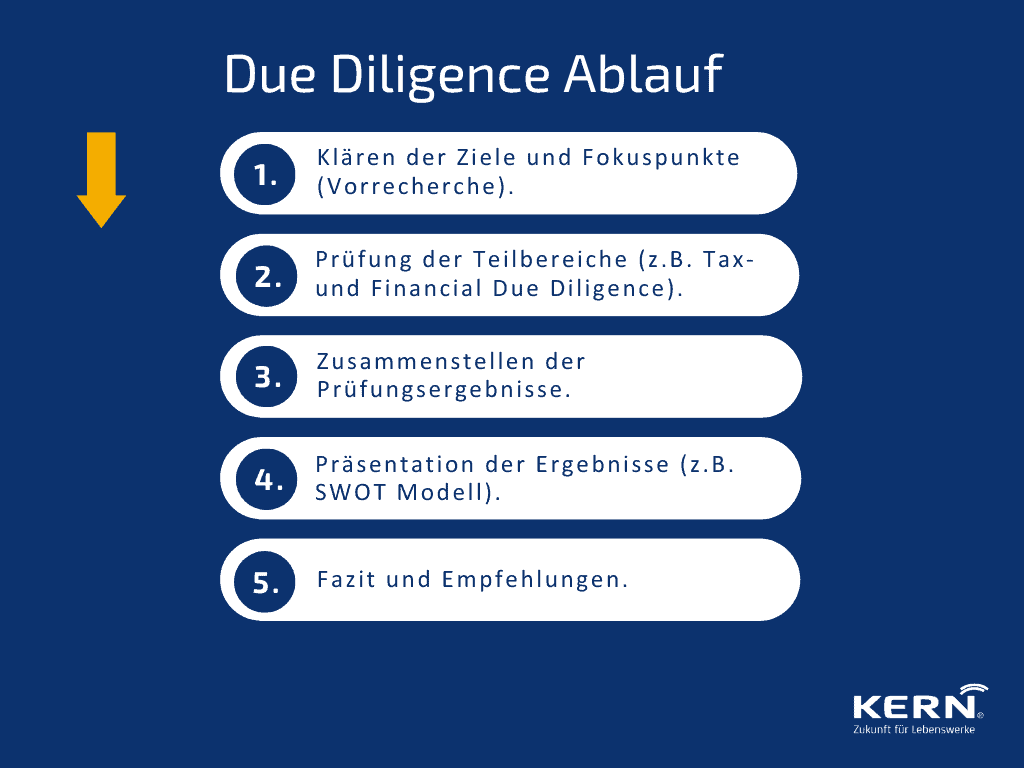
Due Diligence Process
While individual examination patterns can be used depending on the individual case, a 5-step model for the examination process has become established in practice.
After clarifying the objectives and focal points, a preliminary research is carried out by the appointed experts. This preliminary research provides an overview of important sub-aspects and special audit needs.
This is followed by an examination of the individual sub-areas, which culminates in a compilation of the results. The presentation often takes the form of clear models, such as the SWOT analysis model (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats).
Recommendations for further action are derived from these results.
What are the different types of due diligence?
Due to the different focal points of a due diligence audit, individual forms of due diligence have become established in practice. Although they basically follow similar patterns, they differ in detail.
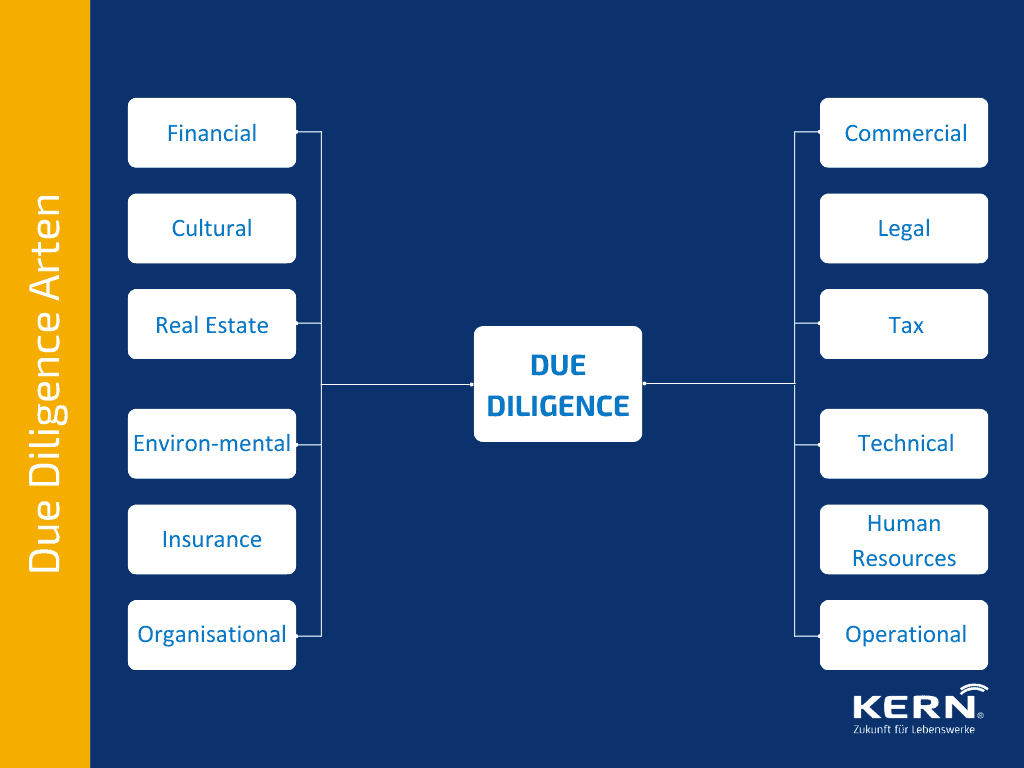
Tax Due Diligence (TDD)
Within the framework of the tax law review, the Tax situation of the target company and its relevant tax influencing factors and risk factors examined. At the same time, TDD structures the Company sale procedure in terms of the purchase price structure for the buyer.
In particular, it is important to structure the company acquisition in such a way that depreciation options for the purchase price and tax-efficient financing are made possible. And, of course, tax risks are also examined.
Technical Due Diligence (TDD)
TDD examines the technical condition of plants and buildings. The aim is to Evaluate technical facilities and buildings and identify potential for repair and modernisation.. This analysis reveals, for example, a hidden investment backlog.
HR Due Diligence (HR DD)
Human resources due diligence is a form of due diligence which A strategic and careful review, evaluation and analysis of a company’s overall human resources strategy and elements. includes. The focus here is on management structures, management processes, human resources instruments and systems, and corporate culture.
Red Flag Due Diligence (RF DD)
A red flag in a DD is a signal from the buy side that can jeopardise the entire M&A process. The relevant due diligence often investigates in advance and quickly targeted obstacles for the further course of the talks. These can be, for example, a problematic financial situation or obvious errors in the documents submitted.
IT Due Diligence (ITDD)
Due to the increasing digitalisation of many business areas, the audit of information technology is becoming more important. The IT Due Diligence examines the IT quality and ?security as well as the future security of a company.
Environmental Due Diligence (EDD)
The EDD examines the environmental quality of the company, its facilities and buildings. Here, for example, it is examined with which Pollution or inherited burdens from previous industrial or technical use of the company. is confronted with. In addition to this, the site is assessed with regard to a future protection status (such as bird sanctuaries, etc.).
Finally, building pollutants (e.g. asbestos in the properties) are surveyed, which can be identified at Demolition or conversion work causes additional costs can. Increasingly, energy efficiency is becoming an important part of EDD. This area is usually dealt with in conjunction with technical due diligence.Commercial Due Diligence (CDD)
With the CDD, the Sales markets analysed for market share, segmentation, growth and competitive situation. In addition, the strengths and weaknesses of the company are examined.
Commercial due diligence is used more in larger transactions. In smaller transactions, the acquirer obtains an overview of the issues examined in this analysis during the preparation of the business plan.
Legal Due Diligence (LDD)
The LDD therefore reviews all legal aspects with internal and external contractual partners of the company for legal risks and pending litigation.
For example Existing tenancy and lease agreements, employee contracts, procurement and supply contracts or, for example, copyright, labour law and antitrust aspects. The company was subjected to a legal due diligence review.
Market Due Diligence (MDD)
Market due diligence is a process of gathering, assessing and analysing market-related information to determine the feasibility of a potential business opportunity.
This includes the Researching and evaluating a target market, analysing competitors’ offerings, assessing customer needs and preferences as well as understanding the competitive landscape.
Financial Due Diligence (FDD)
The FDD validates the data used in the Business valuation information provided and analyses the Financial opportunities and risks of the target company. This includes determining the sustainably achievable income, evaluating cash flows as well as balance sheets and annual financial statements and checking the plausibility of the business plan.
Vendor Due Diligence (VDD)
At the Vendor Due Diligence it is the seller proactively commissioning the audit. An independent third party is commissioned (only then is this VDD sustainable) to comprehensively audit the company in advance. The results are presented to the potential buyer along with all other relevant documentation. This can speed up the process and build confidence. However, the seller bears the higher share of the costs.
Real Estate Due Diligence (IDD)
The IDD examines ownership and leasing relationships with respect to real estate that is either used for the operation of the company or is merely counted as an asset. Condition, obligations or long-term prospects of the properties are only selected pointswhich are examined here.
3 frequently asked questions about due diligence
Due diligence is a translation for “due diligence examination”. It is a process of researching and verifying facts, figures and other information related to a particular business transaction or investment. It is used to reduce or eliminate risk and to ensure that all relevant information is considered before an agreement is reached.
There are different types of due diligence including financial due diligence, legal due diligence or even IT due diligence. Each type of due diligence involves a number of different activities, including research, analysis and evaluation.
The due diligence process usually starts with a thorough review of documents provided by the company. Further research, interviews and audits may then be conducted to complete the full due diligence review.
About the author

Nils Koerber
Born in 1964, trained and studied as a businessman and business economist, certified coach and trainer for succession processes in family businesses, trained mediator (business mediation) and conflict moderator. Co-founder and owner of KERN - Unternehmensnachfolge since 2004. Successful. Practitioner with many years of experience in all aspects of corporate succession in family businesses. Specialised in M&A processes in medium-sized companies. Learn more >